Intercomparison of tropospheric ozone column datasets from combined nadir and limb satellite observations
- Post by: Science Hub Team
- July 30, 2025
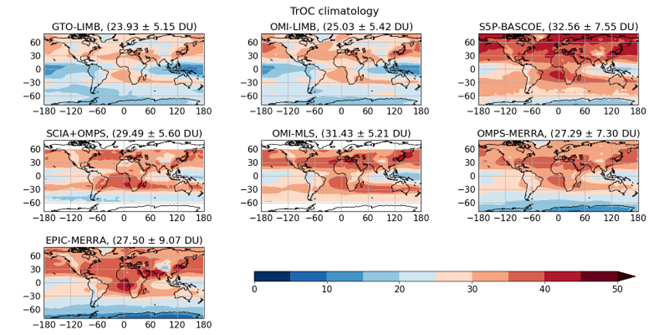
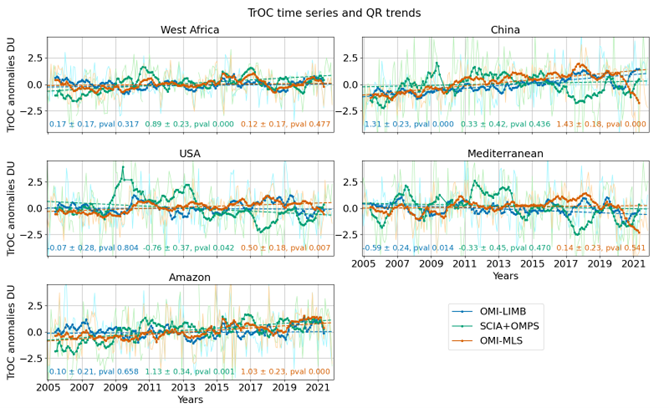
Tropospheric ozone impacts air quality and climate, serving as both a pollutant and a greenhouse gas. In this research, we analysed satellite data of tropospheric ozone columns (TrOC) obtained by combining two types of observations: one providing stratospheric column information and the other total ozone content, thereby obtaining tropospheric ozone as the residual. We compared common climatological features and studied the role of the tropopause definition in explaining biases between datasets and their drifts. When comparing the satellite products with ozonesonde profiles, we found, on average, small drifts, with 1% per decade. We also examined trends over the last 20 years in specific regions, finding generally small trend values, with few regions showing significant and consistent trends, such as South-East Asia.
Carlo Arosio conducted this study during the visit to the Science Hub, and it is part of the OREGANO Project. For more details 👉The OREGANO Project – A Focus on Tropospheric Ozone and its Long-term Trends – ESA Science Hub
Reference and DOI👇
https://amt.copernicus.org/articles/18/3247/2025
Carlo Arosio, Viktoria Sofieva, Andrea Orfanoz-Cheuquelaf, Alexei Rozanov, Klaus-Peter Heue, Diego Loyola, Edward Malina, Ryan M. Stauffer, David Tarasick, Roeland Van Malderen, Jerry R. Ziemke, and Mark Weber, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 18, 3247–3265, https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-18-3247-2025, 202

